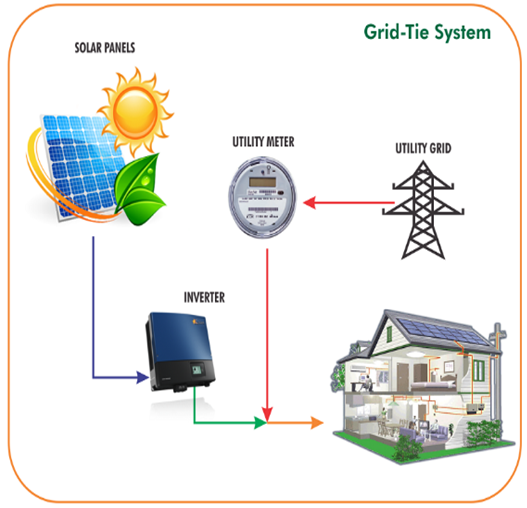
Grid-connected PV systems have become increasingly popular for applications in the built environment. They are connected to the grid via inverters, which convert the DC power into AC electricity. In small systems such as those installed in residential homes, the inverter is connected to the distribution board, from where the PV generated power is transferred into the electricity grid or to AC appliances in the house. In principle, these systems don not require batteries, since they are connected to the grid, which acts as a buffer into which an oversupply of PV electricity is transported. The grid also supplies the house with electricity in times of insufficient PV power generations. However, more and more grid-connected systems also contain batteries in order to increase self- consumption, i.e the amount of PV-generated electricity that is consumed by the household.